Struggling with How To Cite Text Book? You’re not alone. Citing textbooks might seem daunting, but it’s pretty straightforward once you know the rules. This guide will walk you through the essentials of correctly citing a textbook for your academic work. Whether using MLA, APA, or Chicago style, you’ll soon be citing like a pro.
How To Cite Text Book
When writing academic papers, proper citation of textbooks is crucial. It not only gives credit to the original author but also helps you avoid plagiarism. If you’re unsure how to cite an online book in APA 7th edition, this guide will walk you through the nuances of citing a textbook in various formats
Why Citing Textbooks is Important
Citing textbooks properly is essential for several reasons:
- Avoiding Plagiarism: Plagiarism is taking someone else’s work and presenting it as your own. Proper citation ensures you are giving credit where it’s due.
- Credibility: Proper citations strengthen your argument by backing it up with credible sources.
- Reader’s Trust: Readers need to know where you got your information. Citations help them trust your work.
- Academic Integrity: Proper citation adheres to the ethical standards of academia.
Common Citation Styles for Textbooks
Different academic disciplines often use specific citation styles. Here are some of the most commonly used styles:
APA Style
The American Psychological Association (APA) style is widely used in the social sciences. Here’s how to cite a textbook in APA format:
Format:
Author’s Last Name, First Initial. (Year). Title of Book (Edition if applicable). Publisher.
Example:
Smith, J. (2020). Understanding Psychology (10th ed.). McGraw-Hill.
MLA Style
The Modern Language Association (MLA) style is popular in the humanities. Here’s the MLA citation format for textbooks:
Format:
Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Edition, Publisher, Year of Publication.
Example:
Smith, John. Understanding Psychology. 10th ed., McGraw-Hill, 2020.
Chicago Style
The Chicago Manual of Style is often used in history and other disciplines. Here’s how to cite a textbook in Chicago style:
Format:
Author’s Last Name, First Name. Year. Title of Book. Edition. Place of Publication: Publisher.
Example:
Smith, John. 2020. Understanding Psychology. 10th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.
In-Text Citations
Besides the full citation, you’ll often need to include in-text citations. Here’s how to do it in different styles:
APA In-Text Citations
In APA style, include the author’s last name and the year of publication in parentheses.
Example:
(Smith, 2020)
MLA In-Text Citations
In MLA style, include the author’s last name and the page number in parentheses.
Example:
(Smith 45)
Chicago In-Text Citations
Chicago style uses footnotes or endnotes for in-text citations.
Example:
1. John Smith, Understanding Psychology, 10th ed. (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2020), 45.
Citing E-Textbooks
In today’s digital age, you might be using e-textbooks. Here’s how to cite them:
APA Style
Format:
Author’s Last Name, First Initial. (Year). Title of Book. Retrieved from URL
Example:
Smith, J. (2020). Understanding Psychology. Retrieved from http://www.example.com
MLA Style
Format:
Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. E-book ed., Publisher, Year of Publication. URL.
Example:
Smith, John. Understanding Psychology. E-book ed., McGraw-Hill, 2020. http://www.example.com
Chicago Style
Format:
Author’s Last Name, First Name. Year. Title of Book. E-book ed. Place of Publication: Publisher. URL.
Example:
Smith, John. 2020. Understanding Psychology. E-book ed. New York: McGraw-Hill. http://www.example.com
Citing a Chapter in a Textbook
Sometimes, you might need to cite a specific chapter written by a different author in a textbook. Here’s how:
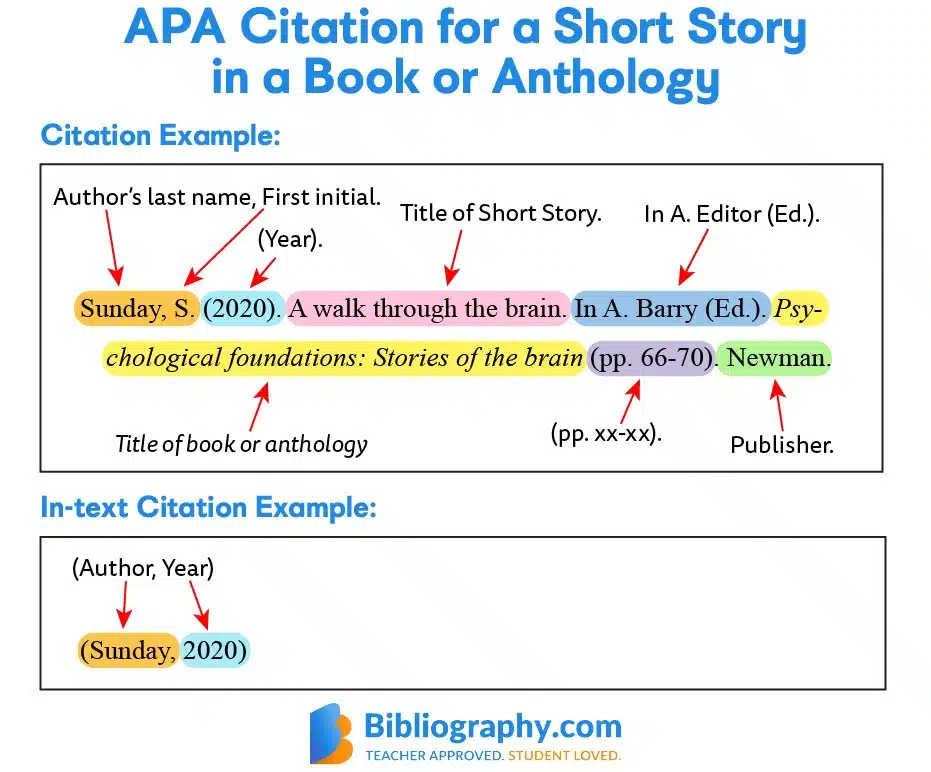
APA Style
Format:
Author’s Last Name, First Initial. (Year). Title of Chapter. In Editor’s Initial. Last Name (Ed.), Title of Book (pp. pages). Publisher.
Example:
Doe, J. (2020). Theories of Learning. In J. Smith (Ed.), Understanding Psychology (pp. 123-145). McGraw-Hill.
MLA Style
Format:
Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Chapter.” Title of Book, edited by Editor’s First Name Last Name, Edition, Publisher, Year of Publication, pages.
Example:
Doe, Jane. “Theories of Learning.” Understanding Psychology, edited by John Smith, 10th ed., McGraw-Hill, 2020, pp. 123-145.
Chicago Style
Format:
Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Chapter.” In Title of Book, edited by Editor’s First Name Last Name, pages. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year.
Example:
Doe, Jane. “Theories of Learning.” In Understanding Psychology, edited by John Smith, 123-145. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2020.
Using Citation Tools
Citation tools can help make the process easier. Here are a few recommended ones:
- EndNote: A reference management software that integrates with Microsoft Word.
- Zotero: A free, easy-to-use tool that helps you collect, organize, cite, and share research.
- RefWorks: An online research management and writing tool.
These tools usually have a function to automatically generate citations in various styles. They can save you a lot of time.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Citing textbooks can be tricky. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
- Missing Author: Always include the author’s name. If there are multiple authors, list them in the order they appear in the book.
- Incorrect Formatting: Follow the specific guidelines for the citation style you are using. Pay attention to punctuation and italics.
- Wrong Edition: Ensure you are citing the correct edition of the textbook.
- Ignoring Page Numbers: Include page numbers where applicable, especially for in-text citations.
- Relying Solely on Citation Tools: While citation tools are helpful, they aren’t always perfect. Always double-check the generated citations.
Practical Examples and Scenarios
Let’s look at a few practical examples and scenarios to better understand how to cite textbooks properly.
Citing Multiple Authors
APA:
Smith, J., & Doe, J. (2020). Understanding Psychology. McGraw-Hill.
MLA:
Smith, John, and Jane Doe. Understanding Psychology. McGraw-Hill, 2020.
Chicago:
Smith, John, and Jane Doe. 2020. Understanding Psychology. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Citing Without an Author
Sometimes you may encounter a textbook without a clear author. Here’s how to handle such situations:
APA:
Title of Book. (Year). Publisher.
MLA:
Title of Book. Edition, Publisher, Year.
Chicago:
Title of Book. Year. Edition. Place of Publication: Publisher.
Special Cases
Translated Textbooks
APA:
Author’s Last Name, First Initial. (Year). Title of Book (Translator’s Initial Last Name, Trans.). Publisher. (Original work published Year)
MLA:
Author’s Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Translated by Translator’s First Name Last Name, Publisher, Year.
Chicago:
Author’s Last Name, First Name. Year. Title of Book. Translated by Translator’s First Name Last Name. Place of Publication: Publisher.
Citing a Reprinted Book
APA:
Author’s Last Name, First Initial. (Year). Title of Book. Publisher. (Reprinted from Title of Original Book, Year)
MLA:
Author’s Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Year. Originally published as Title of Original Book, Year.
Chicago:
Author’s Last Name, First Name. Year. Title of Book. Reprint, Place of Publication: Publisher. Originally published as Title of Original Book, Year.
In-depth understanding of how to cite textbooks accurately can significantly improve the quality of your academic work. Making an effort to cite properly demonstrates your dedication to academic integrity. Keep this guide handy for whenever you work on academic papers, and you’ll be well-prepared to tackle any citation challenge.
Frequently Asked Questions
What information do I need to include when citing a textbook?
When citing a textbook, you need to include the following information: the author’s name, the publication year, the title of the book, the edition (if it’s not the first edition), the publisher’s name, and the location of the publisher. Depending on the citation style you are using, you might need additional details like page numbers or chapter titles.
How do I cite a textbook in APA format?
To cite a textbook in APA format, you should follow this structure: Author(s). (Year). Title of the book (edition). Publisher. For example: Smith, J. (2019). Introduction to Psychology (3rd ed.). Pearson.
What is the correct way to cite a textbook in MLA format?
In MLA format, you should cite a textbook like this: Author(s). Title of the Book. Edition, Publisher, Year of Publication. For example: Smith, John. Introduction to Psychology. 3rd ed., Pearson, 2019.
How do I properly cite a chapter from a textbook?
When citing a chapter from a textbook, include the following: Author(s) of the chapter, year, title of the chapter, editors of the book, title of the book, page numbers of the chapter, and publisher. For example, in APA: Author(s). (Year). Title of the chapter. In Editor(s) (Eds.), Title of the book (pp. pages). Publisher.
What should I do if a textbook has multiple authors?
If a textbook has multiple authors, list them in the order they appear on the title page. In APA, include up to 20 authors before using an ellipsis. In MLA, list all authors if there are three or fewer; for more than three authors, list the first author followed by “et al.”
Final Thoughts
Citing a textbook involves following a specific format, depending on the citation style you use. Remember to include the author’s name, publication year, title, edition (if applicable), and publisher. For APA style, list the author’s last name, first initials, year in parentheses, italicized book title, edition in parentheses, and publisher. In MLA, you need the author’s full name, italicized book title, publisher, and year of publication. By following these guidelines, you can accurately cite a textbook in your academic work. Knowing how to cite text book correctly ensures you give proper credit and avoid plagiarism.